Portal:History of science
The History of Science Portal
The history of science covers the development of science from ancient times to the present. It encompasses all three major branches of science: natural, social, and formal. Protoscience, early sciences, and natural philosophies such as alchemy and astrology during the Bronze Age, Iron Age, classical antiquity, and the Middle Ages declined during the early modern period after the establishment of formal disciplines of science in the Age of Enlightenment.
Science's earliest roots can be traced to Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia around 3000 to 1200 BCE. These civilizations' contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and medicine influenced later Greek natural philosophy of classical antiquity, wherein formal attempts were made to provide explanations of events in the physical world based on natural causes. After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, knowledge of Greek conceptions of the world deteriorated in Latin-speaking Western Europe during the early centuries (400 to 1000 CE) of the Middle Ages, but continued to thrive in the Greek-speaking Byzantine Empire. Aided by translations of Greek texts, the Hellenistic worldview was preserved and absorbed into the Arabic-speaking Muslim world during the Islamic Golden Age. The recovery and assimilation of Greek works and Islamic inquiries into Western Europe from the 10th to 13th century revived the learning of natural philosophy in the West. Traditions of early science were also developed in ancient India and separately in ancient China, the Chinese model having influenced Vietnam, Korea and Japan before Western exploration. Among the Pre-Columbian peoples of Mesoamerica, the Zapotec civilization established their first known traditions of astronomy and mathematics for producing calendars, followed by other civilizations such as the Maya.
Natural philosophy was transformed during the Scientific Revolution in 16th- to 17th-century Europe, as new ideas and discoveries departed from previous Greek conceptions and traditions. The New Science that emerged was more mechanistic in its worldview, more integrated with mathematics, and more reliable and open as its knowledge was based on a newly defined scientific method. More "revolutions" in subsequent centuries soon followed. The chemical revolution of the 18th century, for instance, introduced new quantitative methods and measurements for chemistry. In the 19th century, new perspectives regarding the conservation of energy, age of Earth, and evolution came into focus. And in the 20th century, new discoveries in genetics and physics laid the foundations for new sub disciplines such as molecular biology and particle physics. Moreover, industrial and military concerns as well as the increasing complexity of new research endeavors ushered in the era of "big science," particularly after World War II. (Full article...)
Selected article -
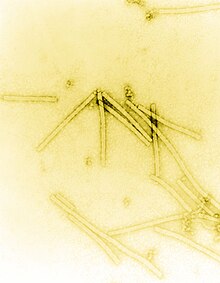
The history of virology – the scientific study of viruses and the infections they cause – began in the closing years of the 19th century. Although Edward Jenner and Louis Pasteur developed the first vaccines to protect against viral infections, they did not know that viruses existed. The first evidence of the existence of viruses came from experiments with filters that had pores small enough to retain bacteria. In 1892, Dmitri Ivanovsky used one of these filters to show that sap from a diseased tobacco plant remained infectious to healthy tobacco plants despite having been filtered. Martinus Beijerinck called the filtered, infectious substance a "virus" and this discovery is considered to be the beginning of virology.
The subsequent discovery and partial characterization of bacteriophages by Frederick Twort and Félix d'Herelle further catalyzed the field, and by the early 20th century many viruses had been discovered. In 1926, Thomas Milton Rivers defined viruses as obligate parasites. Viruses were demonstrated to be particles, rather than a fluid, by Wendell Meredith Stanley, and the invention of the electron microscope in 1931 allowed their complex structures to be visualised. (Full article...)
Selected image

Charles Darwin has been caricatured as a monkey innumerable times since the publications of Origin of Species and Descent of Man.
Did you know
...that Einstein's famous letter to FDR about the possibility of an atomic bomb was actually written by Leó Szilárd?
...that geology was transformed in the latter part of the 20th century after widespread acceptance of plate tectonics?
...that the idea of biological evolution dates to the ancient world?
Selected Biography -
René Descartes (/deɪˈkɑːrt/ day-KART or UK: /ˈdeɪkɑːrt/ DAY-kart; French: [ʁəne dekaʁt] ; 31 March 1596 – 11 February 1650) was a French philosopher, scientist, and mathematician, widely considered a seminal figure in the emergence of modern philosophy and science. Mathematics was paramount to his method of inquiry, and he connected the previously separate fields of geometry and algebra into analytic geometry. Descartes spent much of his working life in the Dutch Republic, initially serving the Dutch States Army, and later becoming a central intellectual of the Dutch Golden Age. Although he served a Protestant state and was later counted as a deist by critics, Descartes was Roman Catholic.
Many elements of Descartes's philosophy have precedents in late Aristotelianism, the revived Stoicism of the 16th century, or in earlier philosophers like Augustine. In his natural philosophy, he differed from the schools on two major points. First, he rejected the splitting of corporeal substance into matter and form; second, he rejected any appeal to final ends, divine or natural, in explaining natural phenomena. In his theology, he insists on the absolute freedom of God's act of creation. Refusing to accept the authority of previous philosophers, Descartes frequently set his views apart from the philosophers who preceded him. In the opening section of the Passions of the Soul, an early modern treatise on emotions, Descartes goes so far as to assert that he will write on this topic "as if no one had written on these matters before." His best known philosophical statement is "cogito, ergo sum" ("I think, therefore I am"; French: Je pense, donc je suis), found in Discourse on the Method (1637, in French and Latin, 1644) and Principles of Philosophy (1644, in Latin, 1647 in French). The statement has either been interpreted as a logical syllogism or as an intuitive thought. (Full article...)
Selected anniversaries
- 1525 - Birth of Tadeáš Hájek, Czech physician and astronomer (d. 1600)
- 1743 - Birth of Martin Heinrich Klaproth, German chemist (d. 1817)
- 1750 - Death of Johan Gabriel Doppelmayr, German mathematician, astronomer, and cartographer (b. 1671)
- 1792 - Birth of Nikolai Ivanovich Lobachevsky, Russian mathematician (d. 1856)
- 1925 - Birth of Martin Rodbell, American scientist, Nobel laureate (d. 1998)
- 1964 - Death of J. B. S. Haldane, Scottish geneticist (b. 1892)
Related portals
Topics
General images
Subcategories
Things you can do
Help out by participating in the History of Science Wikiproject (which also coordinates the histories of medicine, technology and philosophy of science) or join the discussion.
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus